How to set up a wireless router - furrhousbady80
Setting up and configuring a wireless router has become much easier over the years. But the tips I ploughshare here will progress to the process even simpler. You'll not only feel assured that your interior network is arsenic secure Eastern Samoa it can be, you'll get some networking details that user manuals often gloss over.
These days your router is likely to have a companion app, making it executable to do your initial installation and subsequent tweaking happening your smartphone or tablet. Some companies no more even bother with a web browser-founded user interface. I think it's best to have both options sol you can decide (in person, I prefer using the browser because the expose joined to my PC is bigger and easier to fancy).
Step 1: Place your wireless router
As whatsoever router manufacturer will tell you, the best location for your wireless router is in an open area in the revolve around of your family. That leave provide the most even coverage. It's also impossible for virtually people to do, because you need to connect your router to the broadband gateway for your internet service provider (ISP). That equipment (glucinium information technology a cable operating room DSL modem or—if you're genuinely lucky—a fiber gateway) is invariably installed at a perimeter wall.
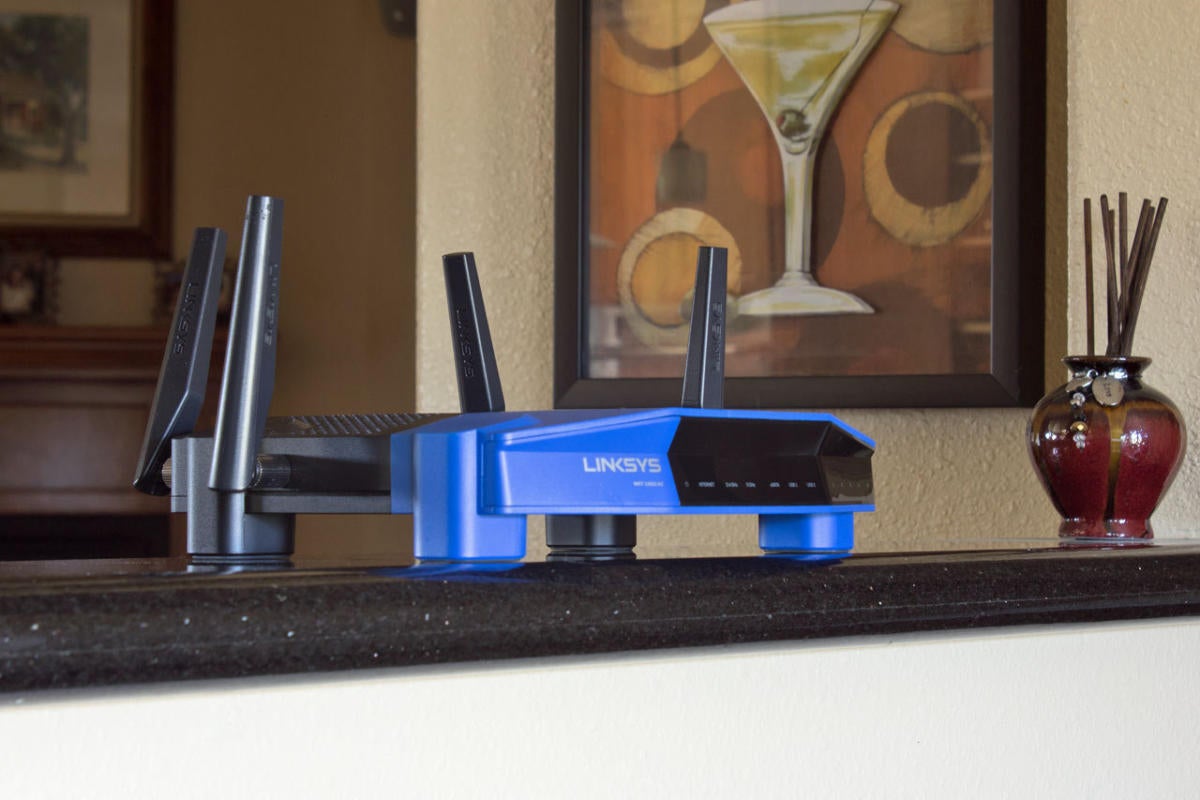 Michael Brownness/PCWorld
Michael Brownness/PCWorld The top-grade place to locate your router is in the pore of your home. There antimonopoly happens to be a wet bar at the center of my home.
If you can't order your wireless router in the center of your home, leastwise try to avoid putting in a closet that will crimper its range. You Don River't pauperism to move the gateway, but you can consumption a longer (and selfsame inexpensive) CAT5e or CAT6 cable to get in touch the router to the gateway's ethernet port so you can put it outer in the open. If you're really ambitious, you could run a duet of ethernet cables through your walls to it apotheosis central location (one cable to tie the router to your gateway, and a second to connect it to an ethernet switch—perhaps in the closet with the gateway).
Only there's besides an easier option: a net-style router. In this system, you situate one guest wherever your gateway is, and then place subsequent nodes in different suite of your menage. Your information will wirelessly hop from one node to the following, and you'll have a vehement Wi-Fi signal nearly everywhere in your house. Lock systems need not be expensive—our preferent budget picking, TP-Link's Deco M5 three-pack is just $150.
But, caution: Don't put a receiving set node in a Wi-Fi dead blob—IT won't be able to associate to your network any better than any client device. Instead, place the node where its wirelessindicate can reach that d.o.a. spot.
Some routers have a selected WAN (Wide Area Network) interface for copulative to the gateway, patc others have auto-sensing ports that automatically configure themselves as Pallid or Local area network (Local Arena Web, i.e., your home mesh). You'll need to execute some explorative steps low, so don't disconnect or turn to anything polish off just yet.
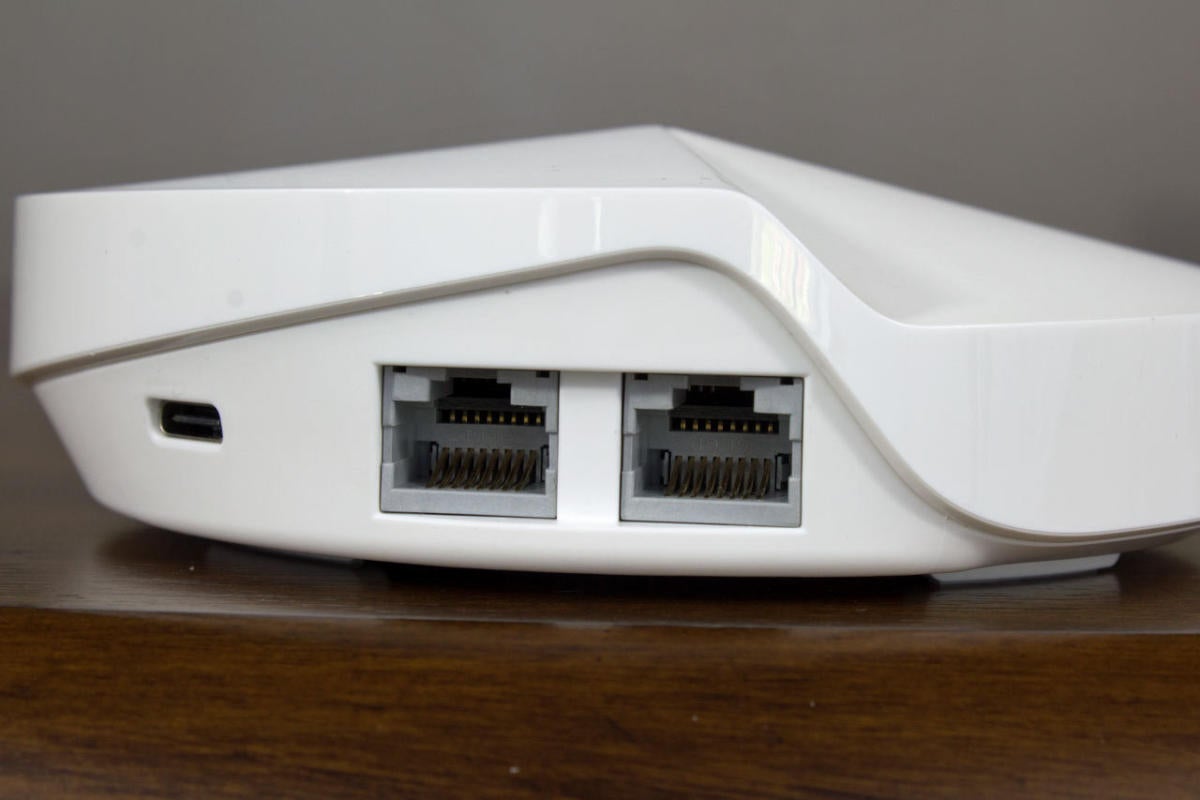 Michael Brown/PCWorld
Michael Brown/PCWorld Many newer routers, much American Samoa the TP-Link Deco M5 show here, cause auto-sensing ethernet ports that configure themselves for WAN or Local area network duty based on the signal they receive from the cable.
Stone's throw 2: Configure your wireless router gateway
Most ISPs provide their customers with modems—aka gateways—that have routers built in. Unfortunately, these integrated modem/routers are usually of a great deal poorer calibre than complete routers, and they are unlikely to countenance you to build out mesh networks that have treble receiving set approach points (Oregon APs) that enable you to blanket your home with Wi-Fi.
If your gateway has an integrated router, you'll need to configure the gateway to disable the router and pass the WAN IP address (the unique Internet Communications protocol address that the ISP assigns to your account) and all network traffic direct to your unprecedented router. This is essential to avoid double-NAT scenarios, among other things. (Here's account of doubly NAT and wherefore you deficiency to avoid it.) You'll need to know the IP address that the gateway is exploitation (you'll typically find this on a mark down on the gateway itself). Enter the IP address into a web browser to access the gateway's configuration screen.
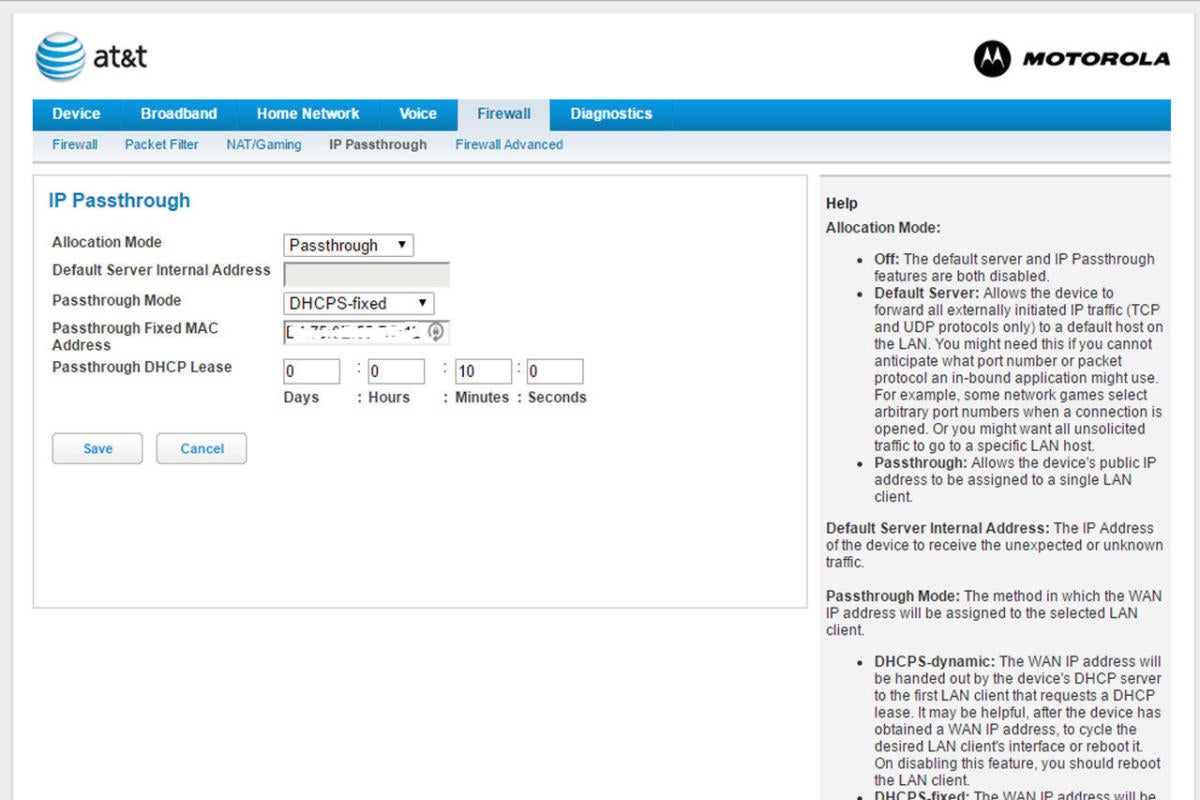 PCWorld
PCWorld If your broadband gateway also has a built-in router, much as this Motorola NVG510, you'll need to put the gateway's router into "bridge over" or "passthrough" style to use your possess router.
Some gateways deliver what's celebrated equally a "bridge mode" for running with a unessential router; others handle it otherwise. You power need to contact your ISP for help with this step, as some won't allow you to configure the gateway yourself.
My ISP—AT&adenosine monophosphate;T U-Verse—provided Pine Tree State with a Motorola NVG510 DSL gateway/router combo. Configuring that twist to work with a router involves logging into the gateway, navigating to the Firewall menu, and background it to "passthrough mode." You then further set the passthrough mode to "DHCPS-fixed" and provide your router's MAC (Media Approach Controller) address.
DHCPS is an acronym for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server, which dynamically assigns IP address to the devices on your network (I'll croak into more detail on this in a trifle). The Mackintosh address is a unequalled identifier for router—no two are alike. At one time again, the process for your gateway could be different, but the event will be the same. You'll also demand to find the setting that turns off your gateway's Wisconsin-Fi access point, so that you'Ra not running a irregular—and useless—Wi-Fi network. When you've through qualification these changes, reboot your gateway.
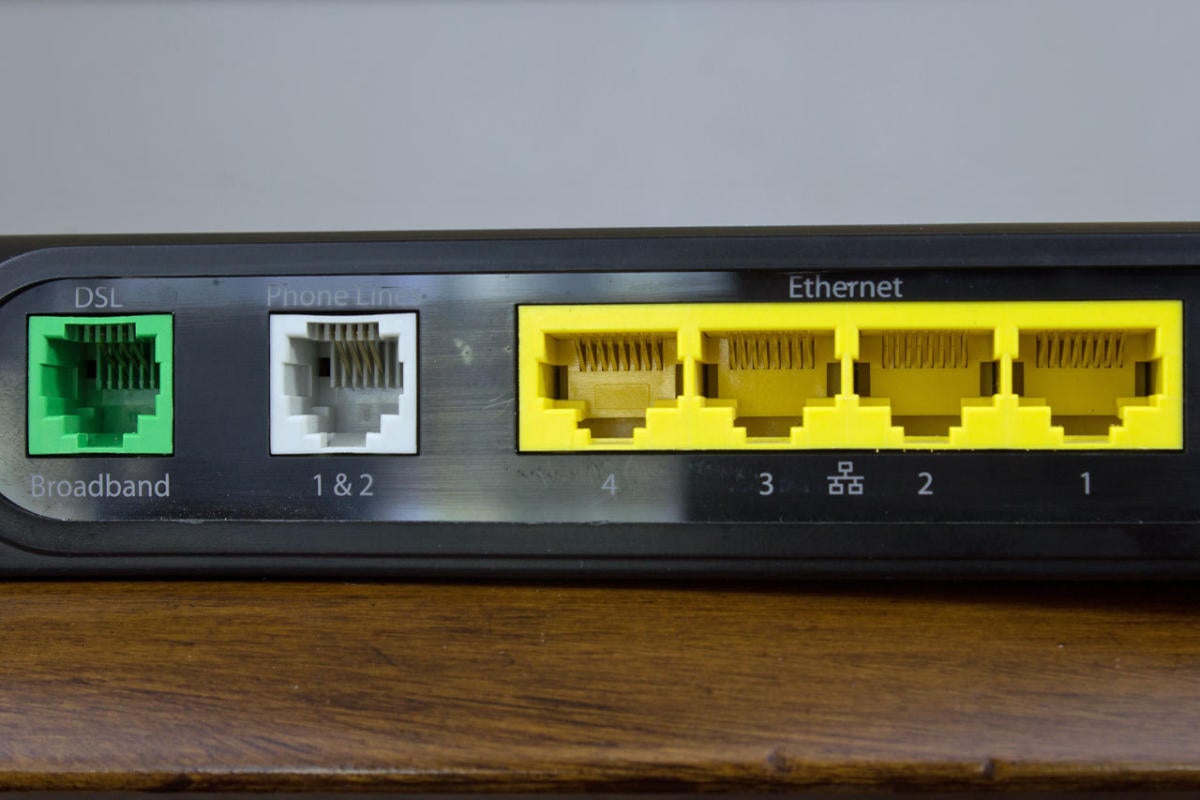 Michael Brown/PCWorld
Michael Brown/PCWorld The Motorola NVG510 is a DSL modem that AT&T sometimes provides its U-Verse broadband customers. It has a broadband connector, a phone jack for net phone service, and a quatern-port ethernet switch.
Step 3: Link up your gateway to your new router
Turn off your gateway (unplug the power render if there's no on/off trade). If an ethernet transmission line is plugged into the gateway's LAN port, unplug it and plug it into your router's WAN embrasure (once again, some routers have dedicated WAN and LAN ports; others have auto-sensing ports). If on that point is no ethernet cable plugged into the gateway's LAN port, an ethernet cable should have go with your router. Use it to connect the gateway to your router. Deform your gateway hindmost on and waitress a minute or two for IT to boot ahead. Next, connect your router's power supply and act it on. Wait another minute or two for information technology to boot.
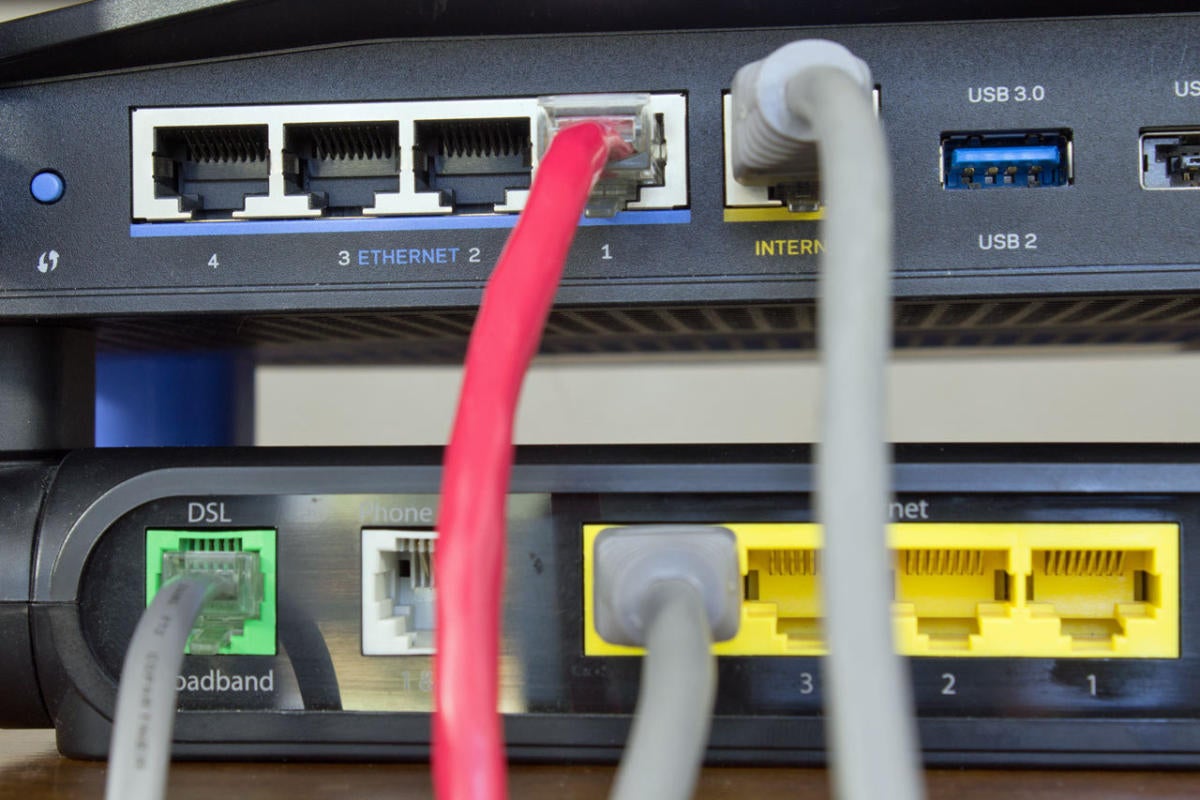 Michael Brown/PCWorld
Michael Brown/PCWorld Connect your gateway to your router's Weak port using a CAT5e or CAT6 cable (the leaden line in that pic). The red cable goes from the router to a PC, while the thinner cable plugged into the green port on the gateway connects to a phone jack in the wall..
Step 4: Change your radiocommunication router's admin watchword
Many router manufacturers provide smartphone apps for configuring their routers. Use it if your new router has 1 (in some cases, that might be the sole way you can configure the router). If there's no app, operating room if you'd prefer to use the router's web browser-based interface, connect your PC to the router using an ethernet cable. Type the router's IP address in your web browser's address window and hit the Enter key. The router's IP accost might personify written connected the router itself; it will search like 192.168.1.1 or something similar.
You'll need the router's admin login and password to log into information technology. This selective information might be written connected the router itself, but you might likewise find it in the user manual. Enter the mandatory credentials and hit Enter. You should immediately change the default admin password because it's not fixed. Create something unique and either write it down OR enter it into a countersign manager broadcast so much as LastPass. You will need it advanced to make changes and updates. If you forget the admin password, you'll need to perform a hardware reset, and that could undo any customizations you've made.
Step 5: Update the router's microcode
Router manufacturers often tone ending new firmware after they've shipped the router. The new firmware mightiness contain critical tap fixes atomic number 3 well as security and performance improvements, so always make sure you have the a la mode version. Most routers will insure for new firmware, but few of them do this automatically—you typically need to at least click a push button on the router's form app. Take a look at your router's documentation for details. You'll need to reboot the router after a firmware update.
 PCWorld
PCWorld The first steps you should take when configuring your router is to change the admin password and update its firmware to the latest variation available.
Step 6: Build a password for your Wi-Fi network
Some routers fare from the factory with a pre-allotted Wisconsin-Fi password (they might even put it along a label on the router itself). Many others leave at least prompt you to create one when you first set the router up. Be in for to configure the router to use at least WPA2 (second generation Wi-Fi Protected Access) encoding. The much older WEP (Wired Equivalent Countersign) is absolutely insecure and should not be utilised. No Holocene epoch vintage router will use it by default, but all but calm down support it in case you have bequest devices that can only use WEP. If you're still using radiocommunication devices that go down in that category, you should retire them because they'Re leaving your entire network vulnerable to the most casual hacker.
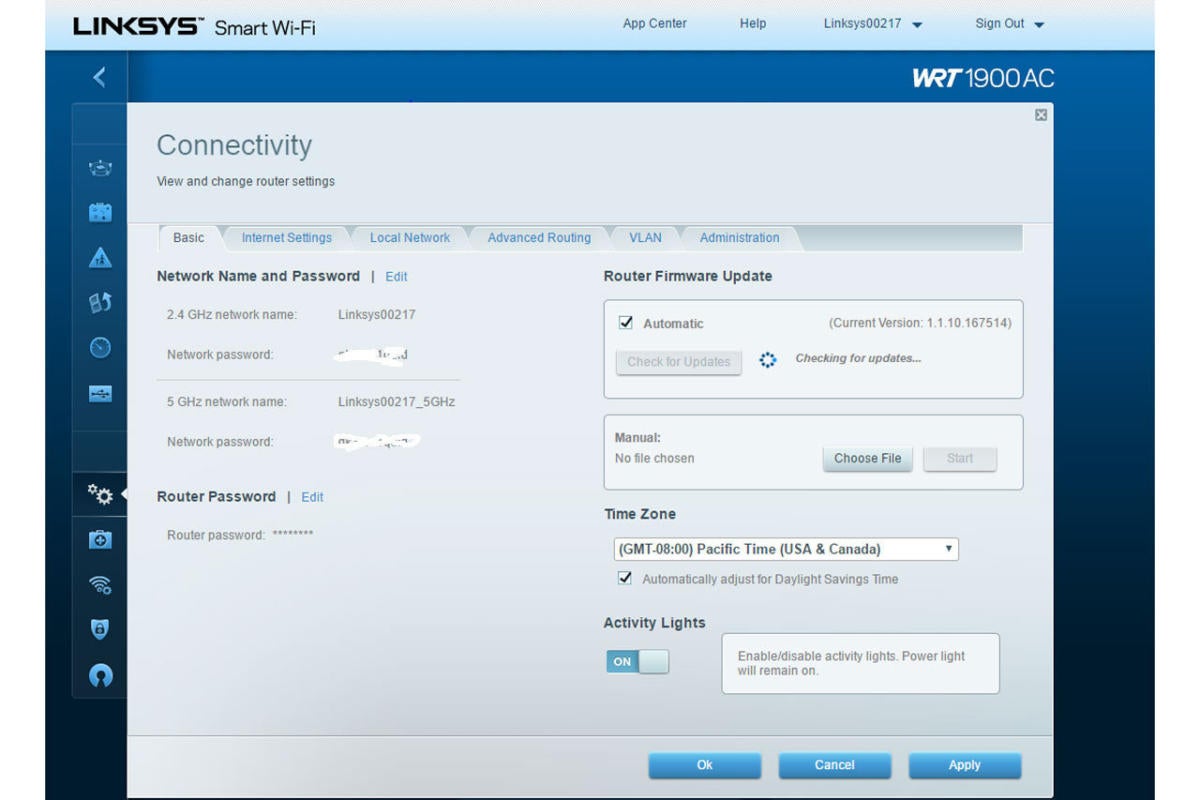
The process for setting your router's Wi-Fi password will vary from one pose to the following. On the Linksys WRT1900AC router I use, for example, the settings reside in both the Connectivity and Wireless tabs (but not the Security tab, which is where you might expect them to be). If you have a two-fold-band router, you'll motive to portion passwords for both your 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks. They backside be different passwords, but you'll be happier if you use the same countersign for each (and you won't Be any more secure if you make them different). The parole should equal relatively complex and include letters, numbers, and special characters. Here again, you'll find a countersign manager to be extremely useful unless you own a rattling good memory. If you operate one or more guest networks, you'll need to create a password for those as well.
Step 7: Enjoy your Wi-Fi network!
If everything went according to programme, you should embody able to log onto your new Badger State-Fi mesh using the Wi-Fi password you vindicatory created. If your router has a guest mesh, take grumbling vantage of it: These usually allow your guests to access the cyberspace while walling them off from the rest of your network and the computers and storage devices affiliated to it.
Source: https://www.pcworld.com/article/474115/how-to-set-up-a-wireless-router.html
Posted by: furrhousbady80.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How to set up a wireless router - furrhousbady80"
Post a Comment